Chapter 16: Policies, Standards, and Compliance
Learning Objectives
After completing this chapter, you will be able to:
- Develop OCM policies that establish organizational requirements
- Create standards that define quality expectations
- Align OCM with regulatory and compliance requirements
- Implement policy enforcement and exception management
- Maintain and improve policies and standards over time
The Role of Policies and Standards
Policies and standards establish the rules and expectations for OCM practice. While governance provides structure and oversight, policies define what must be done, and standards define how well it must be done.
Policies: Mandatory requirements that must be followed. Policies establish minimum expectations and enable accountability.
Standards: Quality expectations that define good practice. Standards guide practitioners toward effective approaches.
Guidelines: Recommended practices that are not mandatory. Guidelines provide helpful direction without creating requirements.
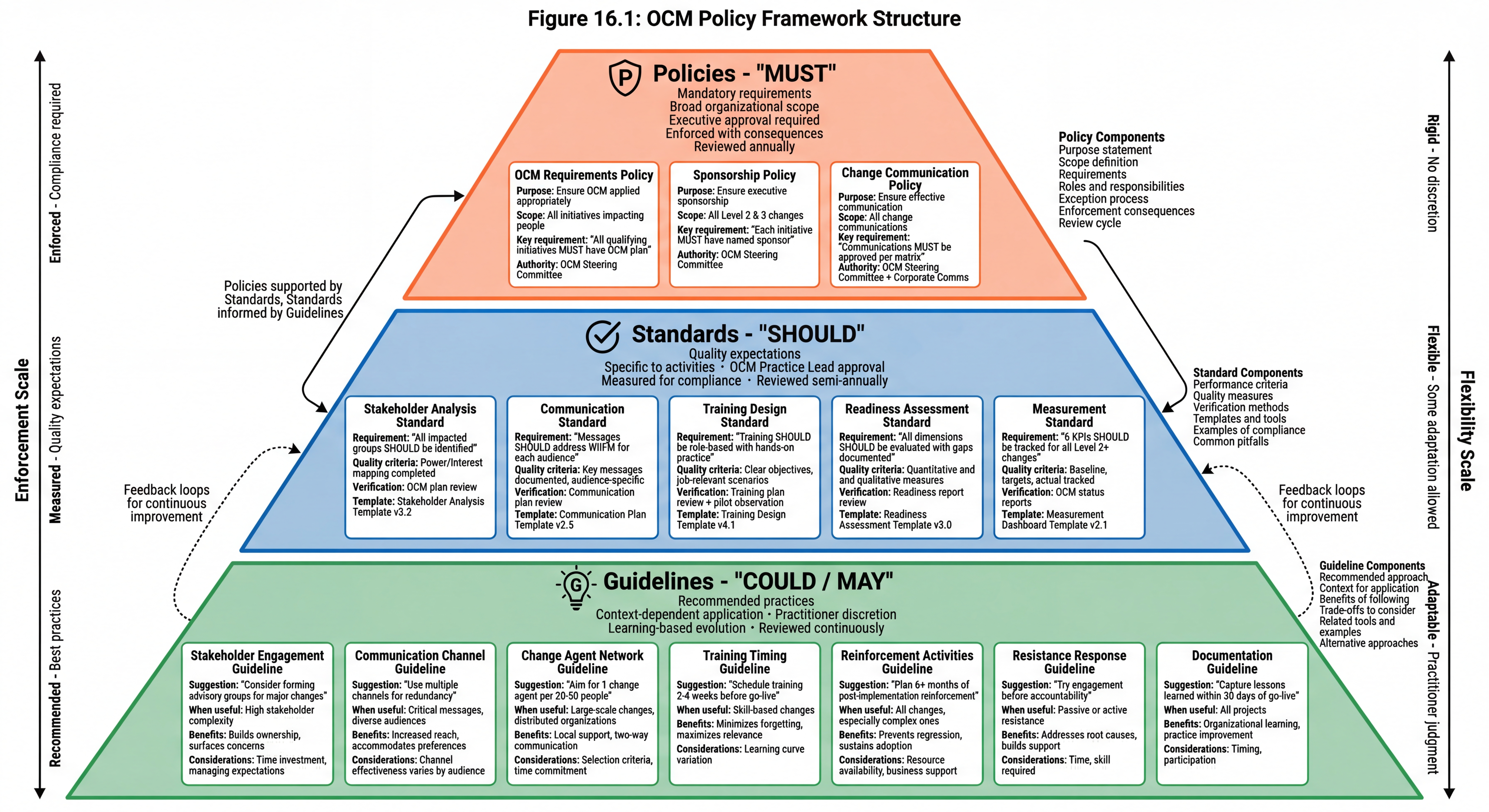
Figure 16.1 - OCM Policy Framework Structure: Policies establish mandatory requirements, Standards define quality expectations, and Guidelines provide recommended practices. Together they govern OCM practice while allowing appropriate flexibility.
OCM Policy Framework
Policy Components
Well-structured policies include:
Purpose: Why the policy exists and what it aims to achieve
Scope: Who and what the policy applies to
Requirements: Specific mandatory requirements
Roles: Who is responsible for compliance
Exceptions: How exceptions are requested and approved
Enforcement: Consequences of non-compliance
Review: When the policy will be reviewed and updated
Sample OCM Policies
Policy 1: OCM Requirements Policy
Purpose: To ensure organizational change management is applied appropriately to initiatives that impact how people work.
Scope: All projects and initiatives that require changes to processes, systems, roles, or behaviors for employees.
Requirements:
- All qualifying initiatives must complete an OCM assessment during initiation
- Initiatives meeting OCM threshold criteria must have a documented OCM plan
- OCM plans must use the organization’s standard methodology and templates
- OCM readiness must be assessed before go-live for all qualifying initiatives
Exceptions: Exceptions require written approval from the OCM Practice Lead.
Policy 2: Sponsorship Policy
Purpose: To ensure appropriate executive sponsorship for organizational changes.
Scope: All initiatives requiring OCM Level 2 or Level 3 support.
Requirements:
- Each qualifying initiative must have a named executive sponsor
- Sponsors must complete sponsor orientation before project kickoff
- Sponsors must commit to minimum activity requirements
- Sponsor effectiveness will be assessed as part of OCM measurement
Policy 3: Change Communication Policy
Purpose: To ensure consistent, effective communication about organizational changes.
Scope: All external and internal communications about organizational changes.
Requirements:
- All change communications must be reviewed and approved per the approval matrix
- Communications must use approved messages from the project message platform
- Major change announcements must be coordinated with Corporate Communications
- Communications must not be distributed before affected managers are briefed
OCM Standards
Standard Categories
Methodology Standards: How OCM activities should be performed
Documentation Standards: What OCM artifacts should contain
Quality Standards: Quality expectations for OCM deliverables
Measurement Standards: How OCM effectiveness should be measured
Sample Standards
Assessment Standards
| Assessment Type | Standard Requirements |
|---|---|
| Stakeholder Analysis | All impacted groups identified; Power/Interest mapping completed |
| Impact Assessment | Process, role, skill impacts documented; Severity assessed |
| Readiness Assessment | All dimensions evaluated; Gaps identified; Action plans documented |
Communication Standards
| Element | Standard |
|---|---|
| Message Development | Key messages documented; WIIFM addressed for each audience |
| Approval | Communications approved per matrix before distribution |
| Timing | Managers briefed before employees |
| Feedback | Two-way mechanism included |
Training Standards
| Element | Standard |
|---|---|
| Design | Role-based design; Clear learning objectives |
| Content | Job-relevant scenarios; Hands-on practice included |
| Delivery | Training scheduled within 2-4 weeks of go-live |
| Assessment | Proficiency assessed post-training |
Compliance Requirements
Regulatory Alignment
OCM practices must align with applicable regulatory requirements:
Data Privacy
- Stakeholder data collected for OCM must comply with privacy policies
- Survey responses must be protected appropriately
- Individual adoption data must be handled according to HR policies
Accessibility
- Training and communication materials must meet accessibility standards
- Multiple formats provided for diverse needs
- Accommodations available for employees with disabilities
Labor Relations
- Union notification requirements followed for applicable changes
- Collective bargaining requirements respected
- Employee consultation requirements met
Audit Readiness
Maintain audit-ready documentation:
Documentation Requirements:
- OCM plans and assessments retained per retention policy
- Communication approvals documented
- Training completion records maintained
- Adoption metrics archived
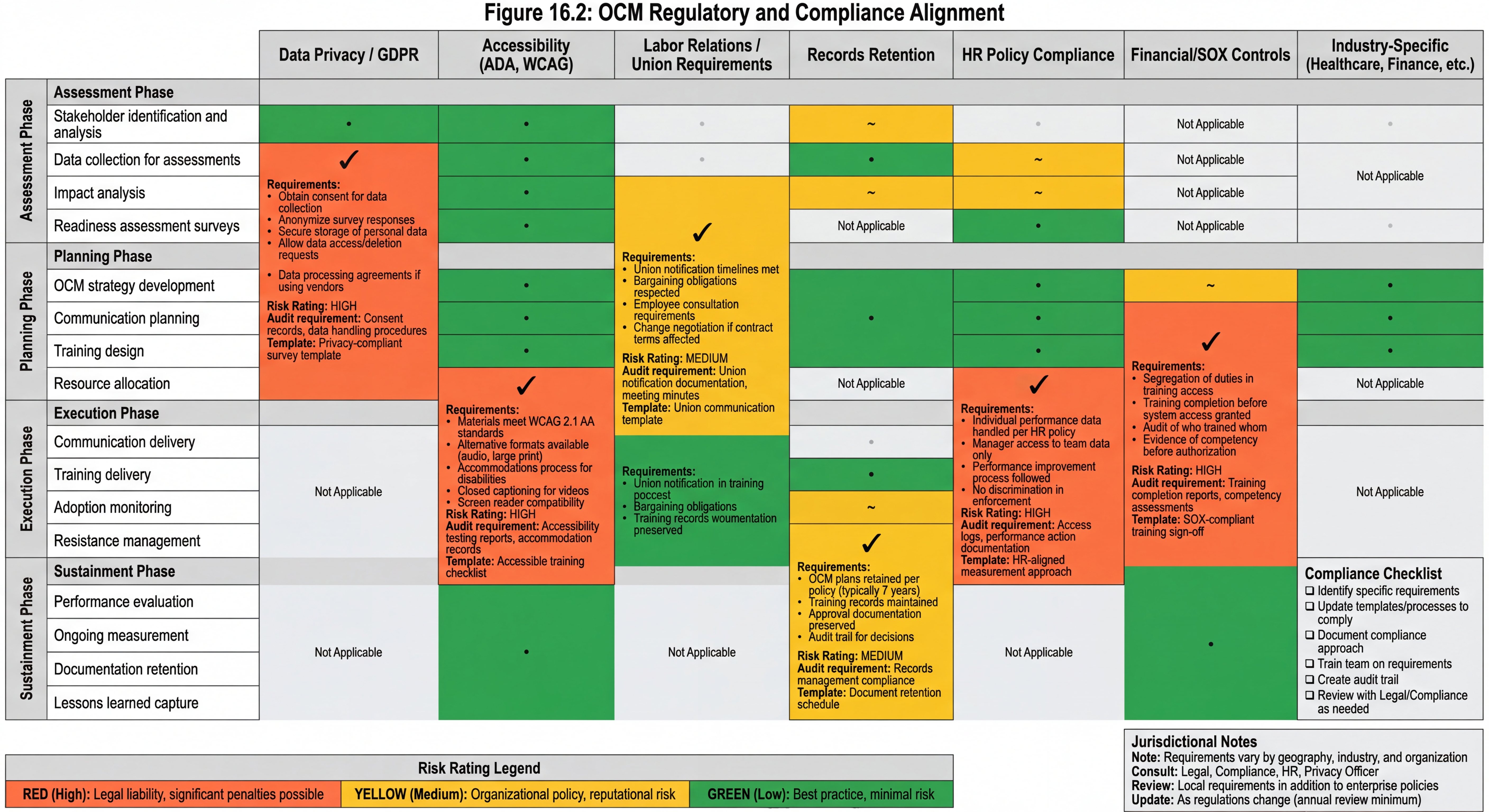
Figure 16.2 - OCM Regulatory and Compliance Alignment: OCM activities must comply with various regulatory and organizational requirements. This matrix identifies where compliance obligations apply and provides guidance for meeting them.
Exception Management
Exception Process
Not all situations fit standard policies. A clear exception process enables flexibility:
- Request: Exception requested in writing with justification
- Review: OCM Practice Lead reviews request
- Risk Assessment: Risks of granting exception evaluated
- Decision: Exception approved, denied, or modified
- Documentation: Decision documented with rationale
Exception Authority
| Exception Type | Approval Authority |
|---|---|
| Minor template deviation | Project OCM Lead |
| Methodology modification | OCM Practice Lead |
| Policy exception | OCM Steering Committee |
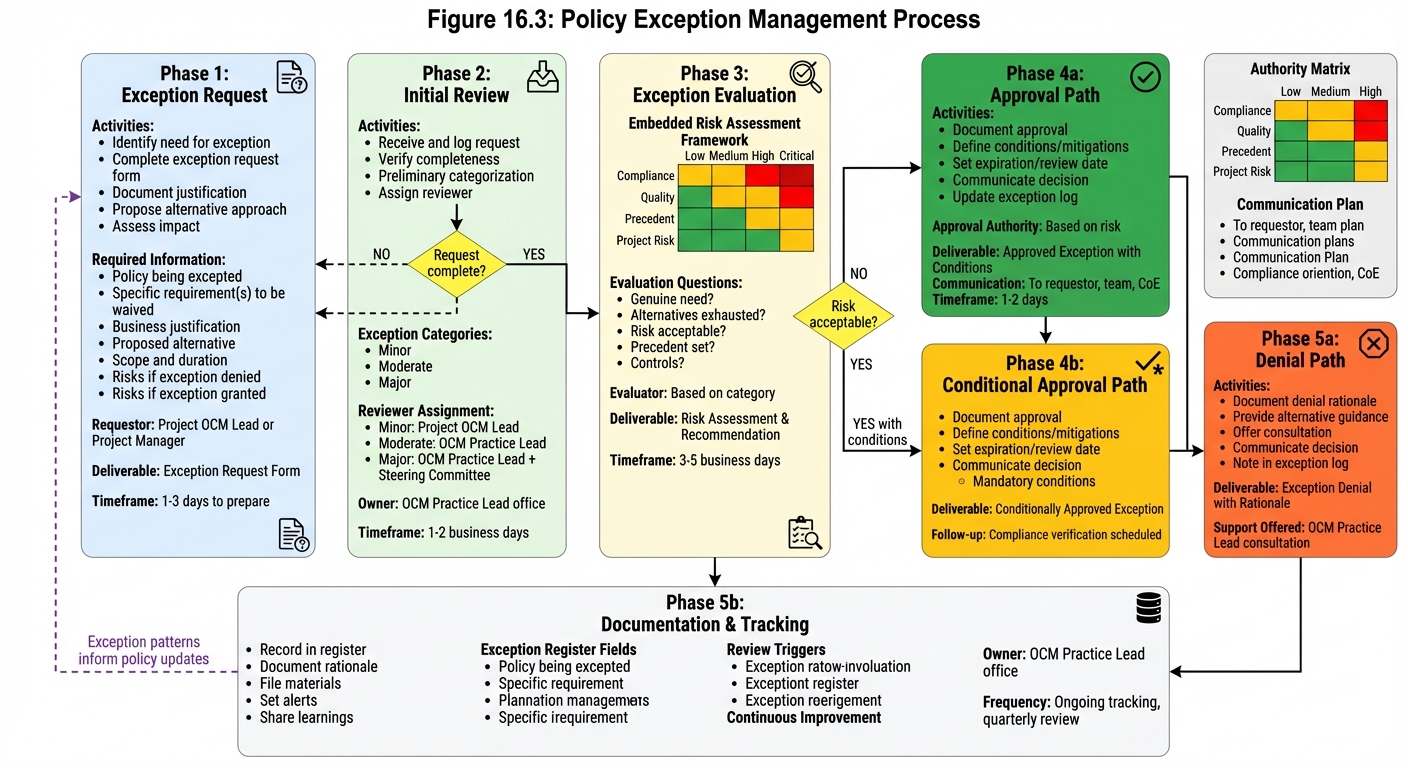
Figure 16.3 - Policy Exception Management Process: Structured exception process balances flexibility with governance. Risk-based evaluation ensures exceptions are granted appropriately with necessary controls and documentation.
Key Takeaways
- Policies establish mandatory requirements that ensure OCM is applied consistently
- Standards define quality expectations that guide practitioners
- Compliance alignment ensures OCM meets regulatory requirements
- Exception management enables flexibility while maintaining accountability
- Regular review keeps policies and standards current
Summary
Policies and standards provide the rules and expectations that enable consistent, effective OCM practice across the organization. Policies establish what must be done; standards establish how well it must be done. Together, they create the framework within which OCM practitioners operate.
Effective policies balance rigor with practicality—clear enough to enable compliance, flexible enough to accommodate different situations, and practical enough to be followed consistently.