Chapter 15: Governance Framework
Learning Objectives
After completing this chapter, you will be able to:
- Establish OCM governance structures and bodies
- Define roles, responsibilities, and decision rights
- Create governance processes for OCM activities
- Integrate OCM governance with project and IT governance
- Monitor and enforce governance compliance
The Need for OCM Governance
OCM governance provides the structures, processes, and authority necessary to ensure that organizational change management is practiced consistently and effectively across the enterprise. Without governance, OCM quality varies by project and practitioner, best practices are not shared, and organizational learning does not occur.
Governance serves multiple purposes:
Consistency: Ensures OCM is applied using common approaches and standards
Quality: Maintains OCM quality through reviews and oversight
Accountability: Establishes clear ownership for OCM outcomes
Integration: Connects OCM with project, IT, and enterprise governance
Continuous Improvement: Enables learning and practice advancement
Governance Structure
OCM Governance Bodies
Depending on organizational size and OCM maturity, governance may include:
OCM Steering Committee
- Strategic direction for OCM practice
- Resource allocation decisions
- Policy approval
- Cross-initiative prioritization
OCM Center of Excellence (CoE)
- Methodology ownership and development
- Practitioner support and consultation
- Training and capability building
- Best practice identification and sharing
OCM Community of Practice (CoP)
- Peer learning and knowledge sharing
- Tool and template development
- Problem-solving collaboration
- Practice improvement suggestions
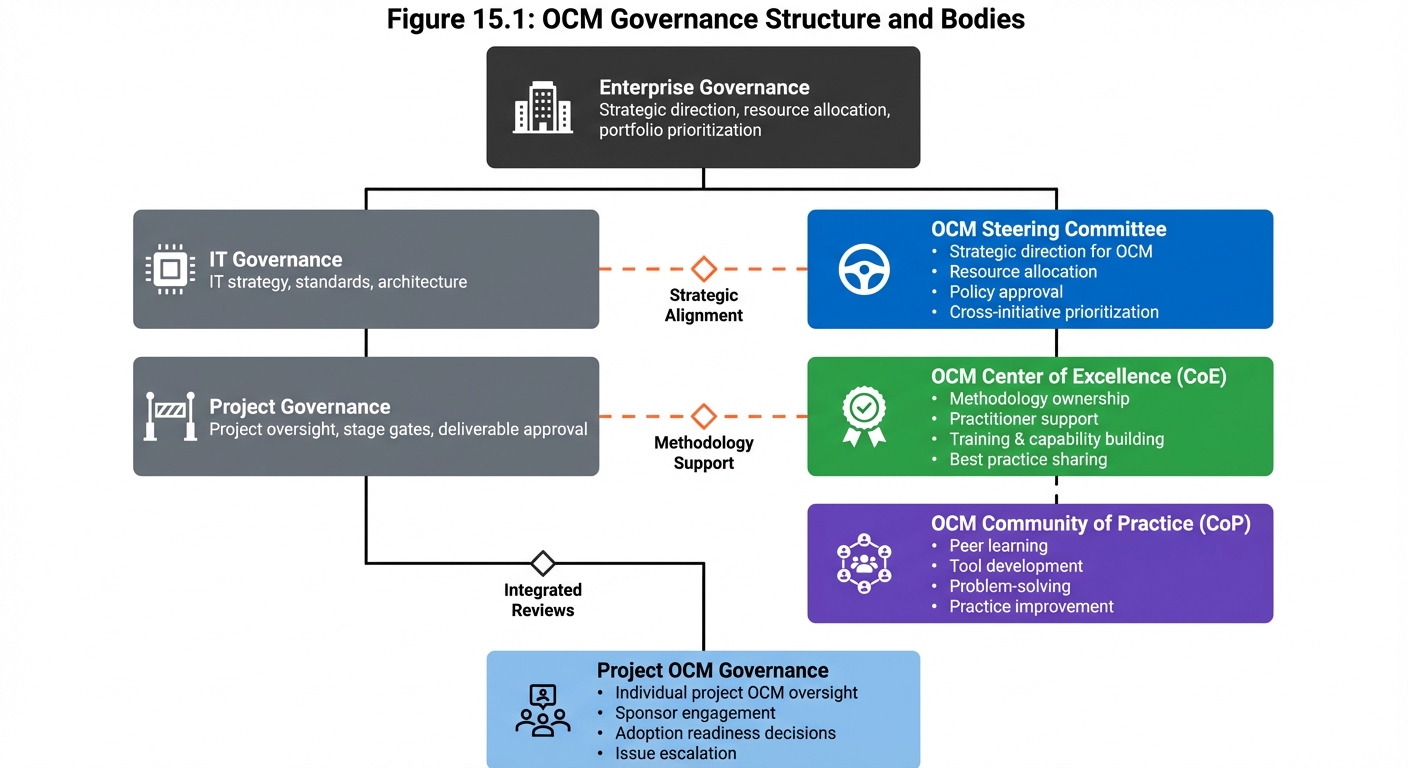
Figure 15.1 - OCM Governance Structure: Effective OCM governance integrates with enterprise and IT governance while providing specialized oversight through dedicated bodies. Clear reporting and coordination relationships ensure alignment.
Project-Level OCM Governance
- Individual project OCM oversight
- Sponsor engagement management
- Adoption readiness decisions
- Issue escalation and resolution
Governance Integration
OCM governance should integrate with existing governance structures:
Enterprise Governance
│
├── IT Governance
│ │
│ └── Project Governance
│ │
│ └── OCM Governance (Project Level)
│
└── OCM Governance (Enterprise Level)
│
├── OCM Steering Committee
│
├── OCM Center of Excellence
│
└── OCM Community of Practice
Roles and Responsibilities
Executive Sponsor
Responsibilities:
- Champion OCM at executive level
- Ensure OCM is resourced appropriately
- Hold leaders accountable for OCM outcomes
- Remove barriers to OCM effectiveness
- Model commitment to OCM practices
OCM Practice Lead / Director
Responsibilities:
- Own OCM methodology and standards
- Lead OCM Center of Excellence
- Develop OCM capability across organization
- Report on OCM effectiveness
- Drive continuous improvement
Project OCM Lead
Responsibilities:
- Develop and execute OCM plans for assigned projects
- Apply OCM methodology and standards
- Report on OCM progress and issues
- Escalate risks and barriers
- Contribute to practice improvement
Project Manager
Responsibilities:
- Integrate OCM into project planning and execution
- Allocate resources for OCM activities
- Support OCM Lead in stakeholder engagement
- Ensure OCM activities are included in project schedule
- Account for OCM in project risk management
Business Sponsor
Responsibilities:
- Own change outcomes and benefits realization
- Provide visible leadership support
- Make timely decisions
- Remove business barriers
- Hold business stakeholders accountable
Line Managers
Responsibilities:
- Support OCM activities for their teams
- Communicate change messages
- Enable training participation
- Coach and support individuals
- Provide feedback on adoption progress
RACI Matrix
| Activity | OCM Practice Lead | Project OCM Lead | Project Manager | Business Sponsor |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OCM Methodology | A/R | C | I | I |
| OCM Plan Development | C | A/R | C | A |
| Stakeholder Assessment | C | A/R | I | C |
| Communication Execution | I | A/R | C | C |
| Training Delivery | C | A/R | C | I |
| Adoption Measurement | C | A/R | I | A |
| Readiness Decision | C | R | R | A |
R = Responsible, A = Accountable, C = Consulted, I = Informed
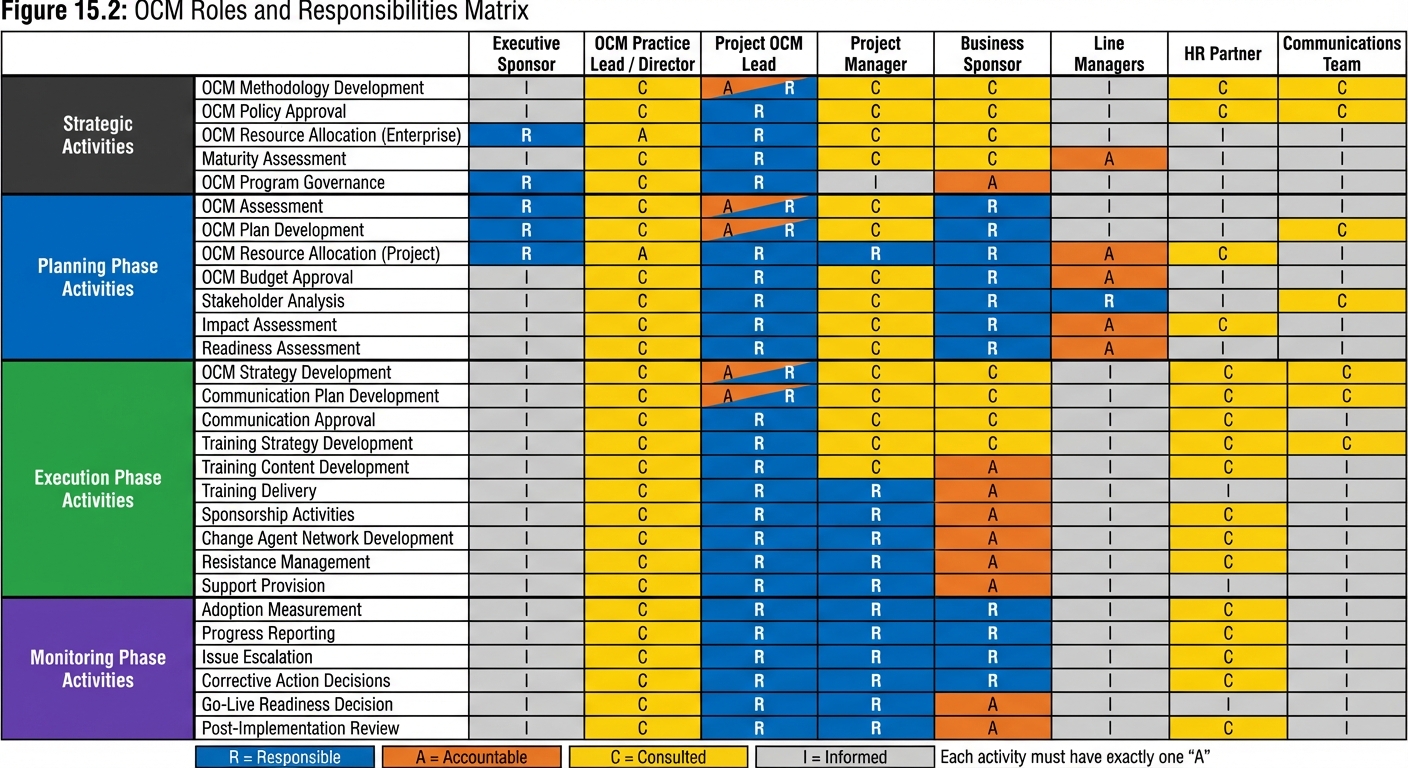
Figure 15.2 - OCM RACI Matrix: Clear assignment of Responsible, Accountable, Consulted, and Informed roles for all major OCM activities ensures accountability and prevents gaps or overlaps in ownership.
Decision Rights
OCM Decision Framework
Clarify who has authority to make different types of decisions:
| Decision Type | Decision Maker | Input Required |
|---|---|---|
| OCM methodology standards | OCM Practice Lead | CoE, CoP |
| Project OCM approach | Project OCM Lead | Business Sponsor, PM |
| OCM resource allocation | Project Manager/Sponsor | OCM Lead |
| Communication content | Project OCM Lead | Business Sponsor, Legal |
| Training approach | Project OCM Lead | Training, SMEs |
| Go-live readiness | Business Sponsor | OCM Lead, PM |
| Resistance escalation | Sponsor | OCM Lead, HR |
| OCM policy exceptions | OCM Practice Lead | Steering Committee |
Escalation Paths
Define clear escalation paths for OCM issues:
Level 1: Project OCM Lead resolves within project team
Level 2: Project Manager and Business Sponsor involvement
Level 3: OCM Practice Lead and functional leadership
Level 4: OCM Steering Committee for cross-functional issues
Level 5: Executive leadership for strategic decisions
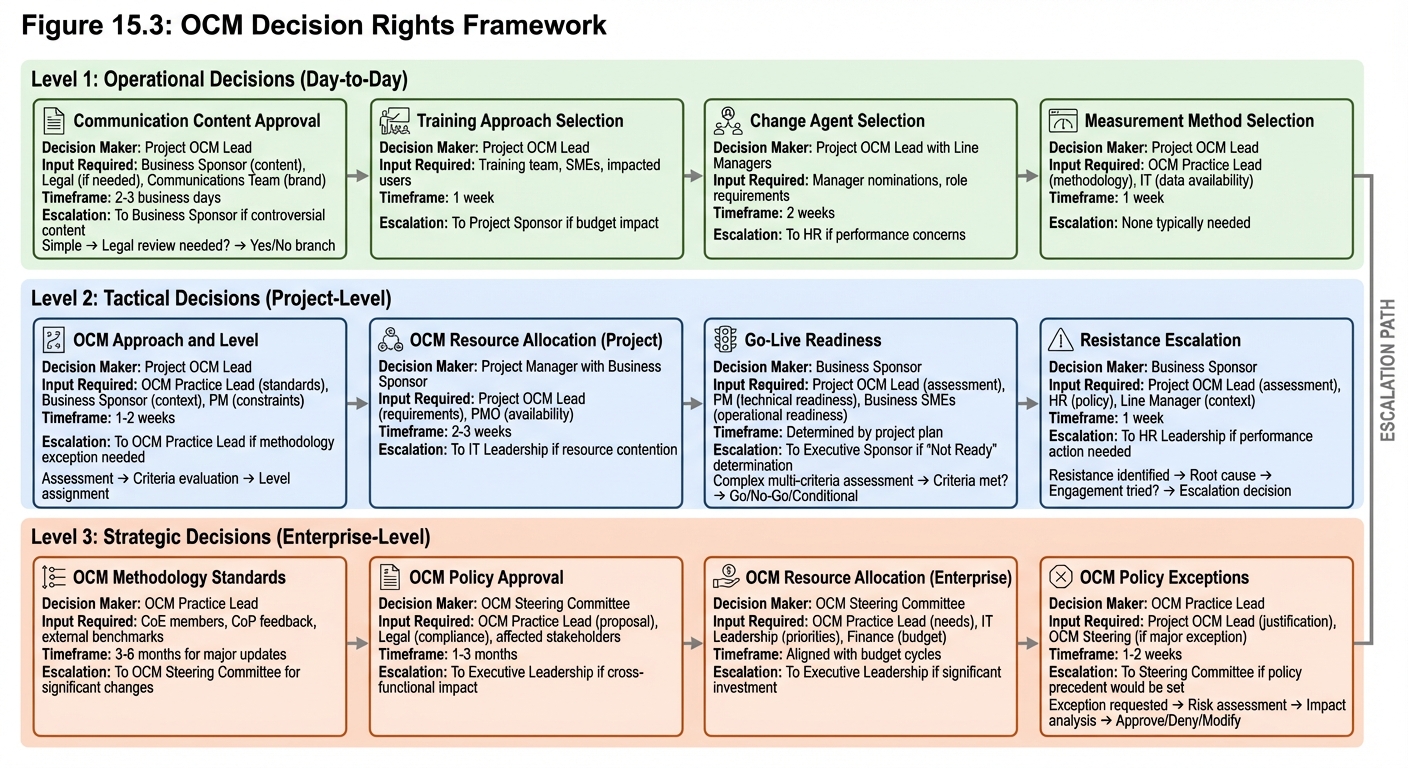
Figure 15.3 - OCM Decision Rights Framework: Clear decision authority eliminates bottlenecks and ambiguity. Operational decisions are made quickly by project teams; tactical decisions involve project sponsors; strategic decisions engage governance bodies.
Governance Processes
OCM Requirements Determination
Process for determining OCM requirements for initiatives:
- Initiative Assessment: Evaluate change characteristics
- OCM Level Determination: Apply criteria to determine required OCM level
- Resource Planning: Identify OCM resource requirements
- Plan Review: Review and approve OCM approach
- Ongoing Oversight: Monitor OCM execution
OCM Level Criteria:
| Factor | Level 1 (Light) | Level 2 (Standard) | Level 3 (Intensive) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Impacted users | <100 | 100-1000 | >1000 |
| Impact severity | Low | Medium | High |
| Stakeholder complexity | Simple | Moderate | Complex |
| Change history | Positive | Mixed | Negative |
| Strategic importance | Low | Medium | High |
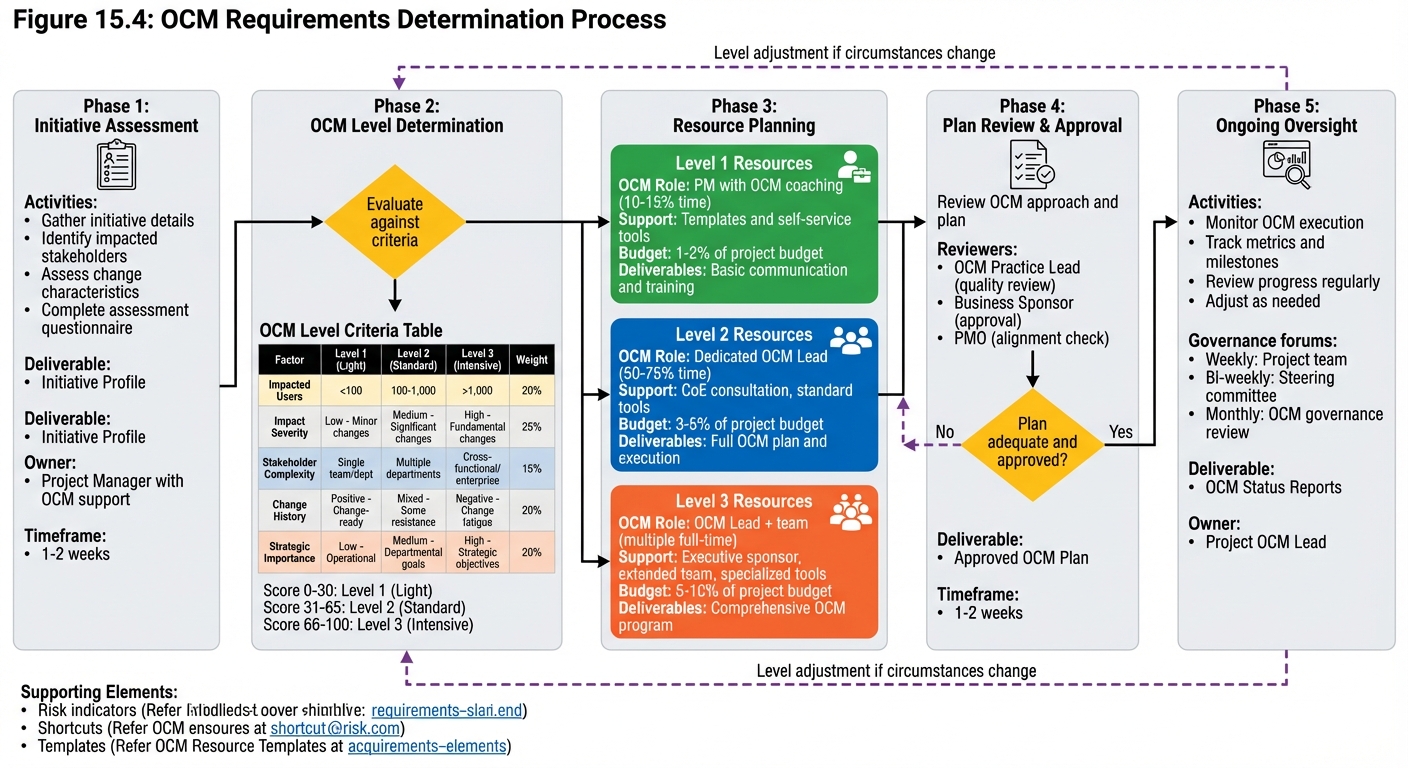
Figure 15.4 - OCM Requirements Determination Process: Systematic assessment determines appropriate OCM level and resources for each initiative. Clear criteria ensure consistent, objective decisions about OCM investment.
OCM Plan Review
Process for reviewing and approving OCM plans:
- Plan Submission: OCM Lead submits plan using standard template
- Quality Review: CoE reviews for completeness and quality
- Sponsor Review: Business Sponsor reviews and approves
- Updates: Plan updated based on feedback
- Approval: Final approval from appropriate authority
- Baseline: Approved plan baselined for tracking
Readiness Assessment
Process for assessing go-live readiness:
- Criteria Definition: Define readiness criteria early in project
- Assessment Execution: Execute readiness assessment activities
- Results Compilation: Compile assessment results
- Gap Analysis: Identify gaps against criteria
- Recommendation: OCM Lead recommendation on readiness
- Decision: Sponsor decision on go-live with OCM input
Sample Readiness Criteria:
- Awareness: >95% of impacted stakeholders aware
- Training: >95% of required training completed
- Proficiency: >80% meeting proficiency standards
- Sponsorship: All required sponsor activities completed
- Support: Support structure in place and tested
- Resistance: Active resistance <15%
Governance Reporting
Standard Reports
Project-Level OCM Status
- Key metrics against targets
- Activities completed/planned
- Issues and risks
- Support needed
Portfolio-Level OCM Dashboard
- OCM status across all initiatives
- Change saturation analysis
- Resource utilization
- Trend analysis
Executive OCM Summary
- High-level adoption status
- Major issues requiring attention
- Strategic decisions needed
- Benefits realization progress
Reporting Cadence
| Report | Audience | Frequency |
|---|---|---|
| Project OCM Status | Project Team, Sponsor | Weekly |
| Portfolio Dashboard | OCM Steering, IT Leadership | Bi-weekly |
| Executive Summary | Executive Team | Monthly |
| Maturity Assessment | OCM Steering | Annually |
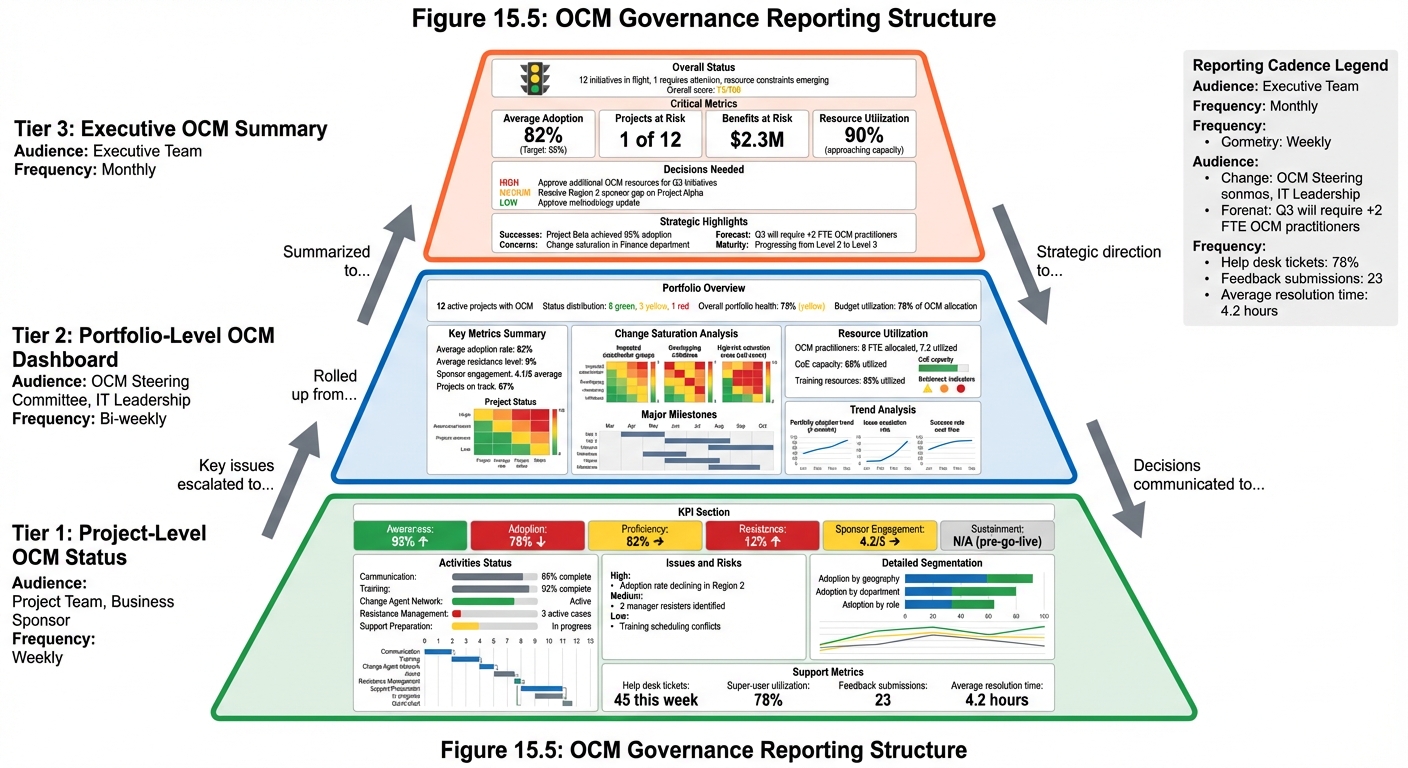
Figure 15.5 - OCM Governance Reporting Structure: Information flows from detailed project reports to portfolio dashboards to executive summaries. Each level provides appropriate detail for its audience while maintaining end-to-end visibility.
Key Takeaways
- Governance structures (steering committees, CoE, CoP) provide oversight and support
- Clear roles and responsibilities ensure accountability for OCM outcomes
- Decision rights clarify who has authority for different decisions
- Governance processes ensure consistent application of OCM practices
- Reporting keeps stakeholders informed and enables oversight
- Balance rigor with enablement—governance should help, not hinder
Summary
OCM governance provides the structures, processes, and authority necessary for consistent, effective organizational change management. Governance bodies at enterprise and project levels provide oversight and support. Clear roles, responsibilities, and decision rights establish accountability. Governance processes ensure OCM is applied consistently across initiatives.
Effective governance balances oversight with enablement—providing enough structure to ensure quality and consistency while not creating bureaucracy that impedes agility. The goal is to help OCM practitioners succeed, not to create administrative burden.